INDIA VIX
Introduction of INDIA VIX

Do you know a single factor which can singly Increase the Price of Call Option and Put Option both and vice versa?It is India VIX, When the India VIX goes up, it tends to increase the prices of both call and put options. Conversely, when the India VIX goes down, it usually decreases the prices of both call and put options. This is because the India VIX reflects market volatility. And higher volatility generally leads to higher option prices due to the increased likelihood of significant market movements.
India VIX, the Volatility Index shows how much the market is expected to change over the next 30 calendar days. When the market is really up and down, the Volatility Index goes up. When things calm down, the index goes down too. The Volatility Index measures how much an index is expected to change over the next 30 calendar days. It’s shown as a percentage and it’s calculated based on how people are trading options for that index. It considers the best bid-ask prices of NIFTY Options contracts expiring to near and next month. However, with 3 trading days left to expiry, It “rolls” to the next and far month. India VIX uses the computation methodology of CBOE with suitable amendments to adapt to the NIFTY options order book.
(‘VIX’ is a trademark of Chicago Board Options Exchange, Incorporated (‘CBOE’) and Standard & Poor’s has granted a license to NSE, with permission from CBOE, to use such mark in the name of the India VIX and for purposes relating to the India VIX.)
Impact of INDIA VIX
The price of options that are close to or slightly away from the current market price tends to be higher on days when the overall market is more uncertain, known as high VIX days. For example, just before an important event like election results, when there’s a lot of uncertainty, the price of these options goes up compared to a few weeks earlier when the market was more stable (low VIX days), even if they have the same amount of time until they expire and the same distance from the current market price. This is because traders are willing to pay more for options to protect themselves against potential big moves in the market during uncertain times.
Computation Methodology
Time to Expiry
The time to expiry is computed in minutes instead of days to arrive at a level of precision expected by professional traders.
Interest Rate
The relevant tenure NSE MIBOR rate (i.e 30 days or 90 days) is being considered as risk-free interest rate for the respective expiry months of the NIFTY option.
The Forward Index Level
India VIX is computed using out-of-the-money option contracts. Out-of-the-money option contracts are identified using forward index level. The forward index level helps in determining the at-the-money (ATM) strike which in turn helps in selecting the option contracts which shall be used for computing India VIX. The forward index level is taken as the latest available price of NIFTY future contract for the respective expiry month.
Bid-Ask Quotes
The strike price of NIFTY option contract available just below the forward index level is taken as the ATM strike. NIFTY option Call contracts with strike price above the ATM strike and NIFTY option Put contracts with strike price below the ATM strike are identified as out-of-the-money options and best bid and ask quotes of such option contracts are used for computation of India VIX. In respect of strikes for which appropriate quotes are not available, values are arrived through interpolation using a statistical method namely ‘Natural Cubic Spline’.
(Natural Cubic Spline” is a way of connecting points on a graph smoothly using curved lines. It’s called “natural” because it doesn’t force the curve to bend in any specific way, and “cubic” because it uses cubic polynomials to create these curves. This method is often used in data analysis and statistics to interpolate between data points in a way that preserves the overall shape of the data.)
Calculation of INDIA VIX
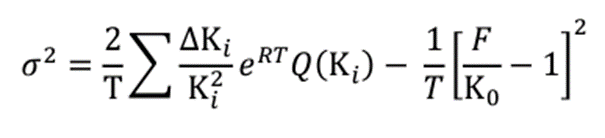
Here,
India VIX = σ x 100
T = Time to expiration
Ki = Strike price of ith out-of-the-money option
( a call if Ki > F and a put if Ki < F ) ΔKi = Interval between strike prices- half the distance between the strike on either side of Ki
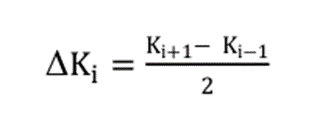
(Note: Δ for the lowest strike is simply the difference between the lowest strike and the next higher strike. Likewise, Δ for the highest strike is the difference between the highest strike and the next lower strike)
R = Risk-free interest rate to expiration
Q(Ki) = Midpoint of the bid ask quote for each option contract with strike Ki
F = Forward index taken as the latest available price of NIFTY future contract of corresponding expiry
K0 = First strike below the forward index level, F.
Source : NSE India
Conclusion
In Short INDIA VIX is the thermometer of uncertainty in Share Market in next few weeks. If any one do mastery in VIX, he may convert the losses into profit. Mastering VIX trading can help mitigate losses or profit from market volatility, but success isn’t guaranteed and requires skill, discipline, and risk management.
Click here to Know Why Bank Nifty is so volatile?
Link to Read our Top Article:
- Agriculture Sector: Best Stocks in Agro Sector
- Liquor Sector: Best Alcoholi Stocks in India
- Railway Sector & Rail Stocks in India
- IT Sector: Best it stocks in india
- FMCG Sector: Top FMCG Stocks in India
- Indian ADR Stocks
- Renewable Energy Stocks India
- Semiconductor Stocks in India
- 10 Top EV Stocks in India – Best EV Penny Stocks list in India
- Investment in International Stock Market: Advantages & Associated Risks
- Global Investment
- INDIA VIX
- Dollar Index (DXY / USDX)
- Bank Nifty Calculation & Formula
- Top 10 Auto Stocks & the Sector in India: Trends and Opportunities



